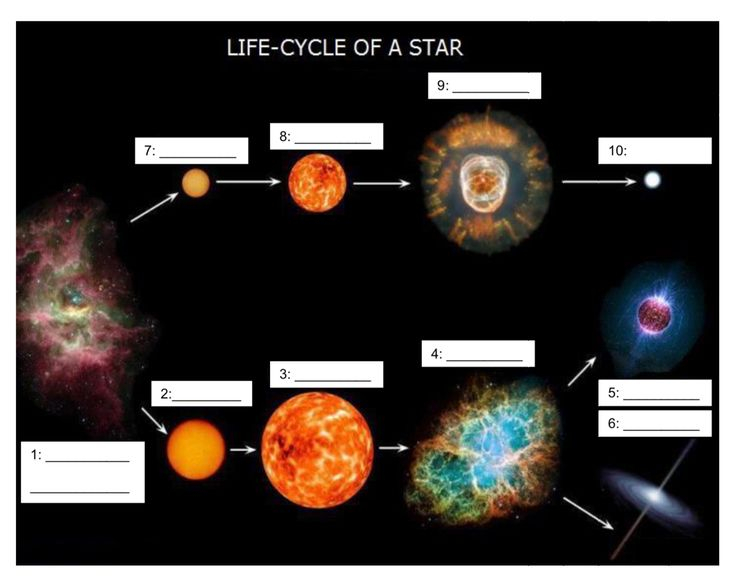
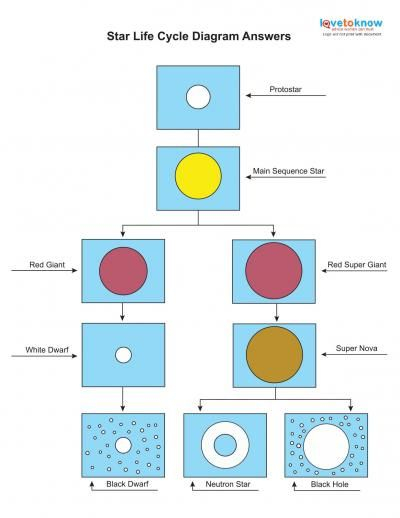
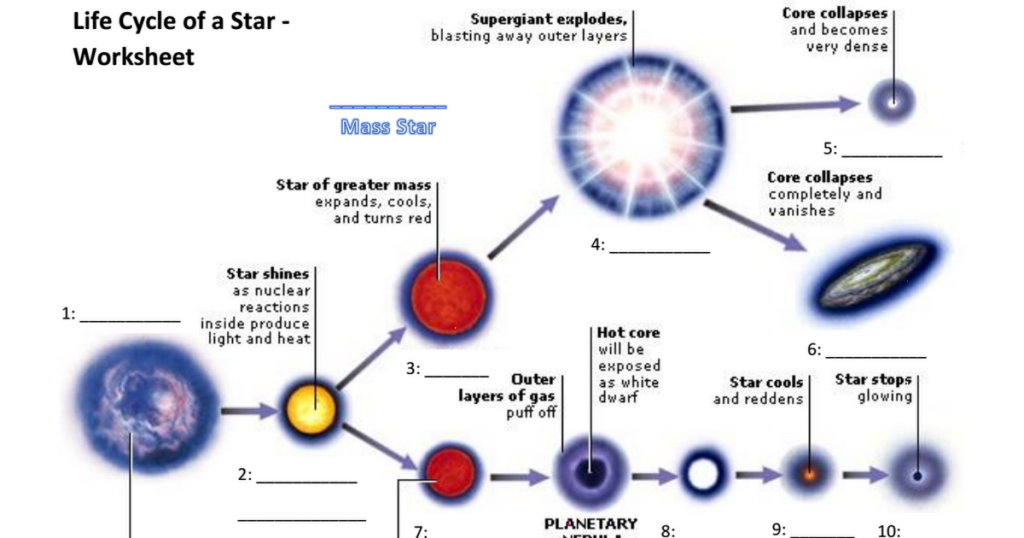
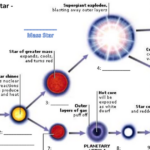
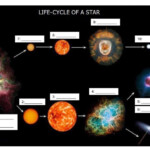
Star Life Cycle Worksheet Pdf – Students are taught about the life cycles of different creatures. A butterfly’s lifecycle can be compared with that of a shark. They can also learn about the life cycle of an amphibian. This worksheet can help students learn how animals live. Students can complete the worksheet independently and as a class.
The life cycle of a human
Fertilization is the moment when an egg cell from a woman merges with a male sperm cell. This begins the human life cycle. The sixth day is when the single cell splits into several smaller cells that burrow into the mother’s womb. These cells begin to form three layers and then bend into an embryo. They also start to differentiate and create the fetal nervous and circulatory systems.
During this period, the human brain and body undergo many changes. While there are some differences between humans and apes in their lives, they all follow the same basic cycle. For example, humans develop an erect body and show off their movable hands, whereas apes develop great cognitive talents. The food we eat supports a host of changes in the human body and brain after conception.
The human life cycle is organized around a series developmental stages and age groups. It also includes an infancy period. The average life span of a human is about seventy to eighty years, but this can vary widely depending on the health of the individual.
The life cycle of a butterfly
The Life cycle of a butterfly begins with the butterfly’s egg. The caterpillar’s needs are met by the egg. Most butterflies lay eggs on leaves. The eggs can be small, round, oval or cylindrical. Monarch butterflies lay their eggs on the underside of plant leaves. They can be either smooth or wrinkled. Within a few weeks, the eggs will hatch.
After the butterfly emerges from its pupa, it injects its blood into its wings. After a few hours, the wings will fully develop and the butterfly will begin to fly. After the wings are fully developed, the butterfly will begin to search for food and a partner. After finding a mate, the butterfly will lay eggs on a leaf.
The next stage is the adult stage. The butterfly lays eggs in spring, summer, and fall. The female butterfly lays a large number of eggs at one time. Although the eggs are small, they can be very large. The caterpillar, also known as the larva, develops from the egg. During this time, it eats continuously and sheds its skin four or five times. It also stores food, which will be used by the adult butterfly.
Sharks live a long life
Sharks have an extremely long life cycle. They can live for up to fifteen years. Sharks are most commonly born near the coast and stay close to their birthplace until they reach adulthood. Sharks mature, reproduce, and grow during this period. Sharks have two claspers, which allow them to grab onto a female and insert sperm.
Female sharks incubate the eggs and sperm for a period of several months until they reach full term. The young sharks remain inside the mother for a year and a half before they are born alive. Cannibalism is a behavior in which a shark’s first pup is alive and eats other pups or eggs. The gestation period of these ovoviviparous species varies, but it is often several months to two years. Asexual reproduction is also possible in some species.
Sharks have excellent hearing and are able to detect incoming sound waves from their prey. Their two sets of dorsal fins are located on either side of their heads. Their lateral line system consists of thin canals filled with water and is attached to nerves that send signals to the brain.
Life cycle of an amphibian
The life cycle of most amphibians is complex, with a larva becoming an adult and then a larva becoming a larva. Hormones and the environment control these life cycles. Thyroid hormones and corticosteroids produced by interrenal glands are the primary morphogens in amphibians and are dependent on input from the hypothalamus and pituitary glands. The hypothalamus controls the activity of the thyroid and pituitary glands.
Amphibians have unique life cycles and a unique ability to reproduce in two environments – on land and in water. The life cycle of a frog begins with sexual reproduction, in which the male entices the egg-carrying females to mate. The females release their eggs into water, where the males fertilize with sperm. External fertilization is the most common method of reproduction for amphibians.
Many species of frogs lay eggs in calm water which protects them against predators. However, some species stay with the eggs to care for them. Once fertilized, the eggs begin to split into more cells, taking on the form of a tadpole. The tadpoles hatch within one to three weeks.